OEM Toy Manufacturing Process: Step-by-Step Guide from Design to Mass Production
OEM Toy Manufacturing Process: Step-by-Step Guide from Design to Mass Production
In today’s competitive toy market, bringing a concept to life requires a streamlined, efficient, and reliable manufacturing process. Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) partnerships enable brands to transform innovative designs into high-quality, market-ready toys without owning production facilities. This comprehensive guide details the step-by-step journey from a mere idea to mass-produced toys, optimized for search engines and designed to help your business navigate this complex landscape.
1. Concept Development & Design
Every successful toy begins with a solid concept.
Market Research & Ideation: Identify trends, age groups, and safety standards (like ASTM F963, EN71). Define your toy’s unique selling proposition (USP).
Concept Sketching: Create hand-drawn or digital sketches to visualize form, function, and aesthetics.
3D CAD Modeling: Professional designers convert sketches into precise 3D models. This digital blueprint details every dimension, mechanism, and part assembly.
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) Analysis: Experienced OEMs review the 3D model to suggest optimizations for cost-effective, efficient, and safe mass production.
2. Prototyping
Transforming the digital model into a tangible sample is critical.
Rapid Prototyping: Techniques like 3D printing (SLA/SLS) create initial physical models from the CAD file. This "looks-like" prototype assesses form and feel.
Engineering Prototype: A "works-like" prototype, often using machined parts or off-the-shelf components, tests functionality and mechanics.
Pilot Run Prototype: Produced on the actual production line with intended materials and processes, this final sample is for comprehensive evaluation.
3. Engineering & Pre-Production
This phase ensures the toy is ready for the factory floor.
Tooling Creation: Engineers design and manufacture custom molds for plastic injection (hard steel or softer aluminum molds) and dies for metal parts. This is a significant upfront investment and time commitment.
Material Sourcing: The OEM selects and certifies raw materials (plastics, paints, fabrics, electronics) that meet safety, quality, and cost requirements. All materials must comply with relevant regulations (e.g., REACH, CPSIA).
Production Line Setup: The factory configures assembly lines, schedules workforce, and programs automated machinery.
4. Safety & Compliance Testing
Non-negotiable for global market access and consumer trust.
Laboratory Testing: Independent accredited labs conduct rigorous tests for:
Physical & Mechanical Safety: Small parts, choking hazards, sharp edges, strength.
Chemical Safety: Heavy metals (lead, cadmium), phthalates, flammability.
Electrical Safety: For battery-operated or electronic toys (FCC, CE).
Certification: Upon passing, receive official certificates (e.g., CPC for USA, UKCA for UK, GCC for Australia).
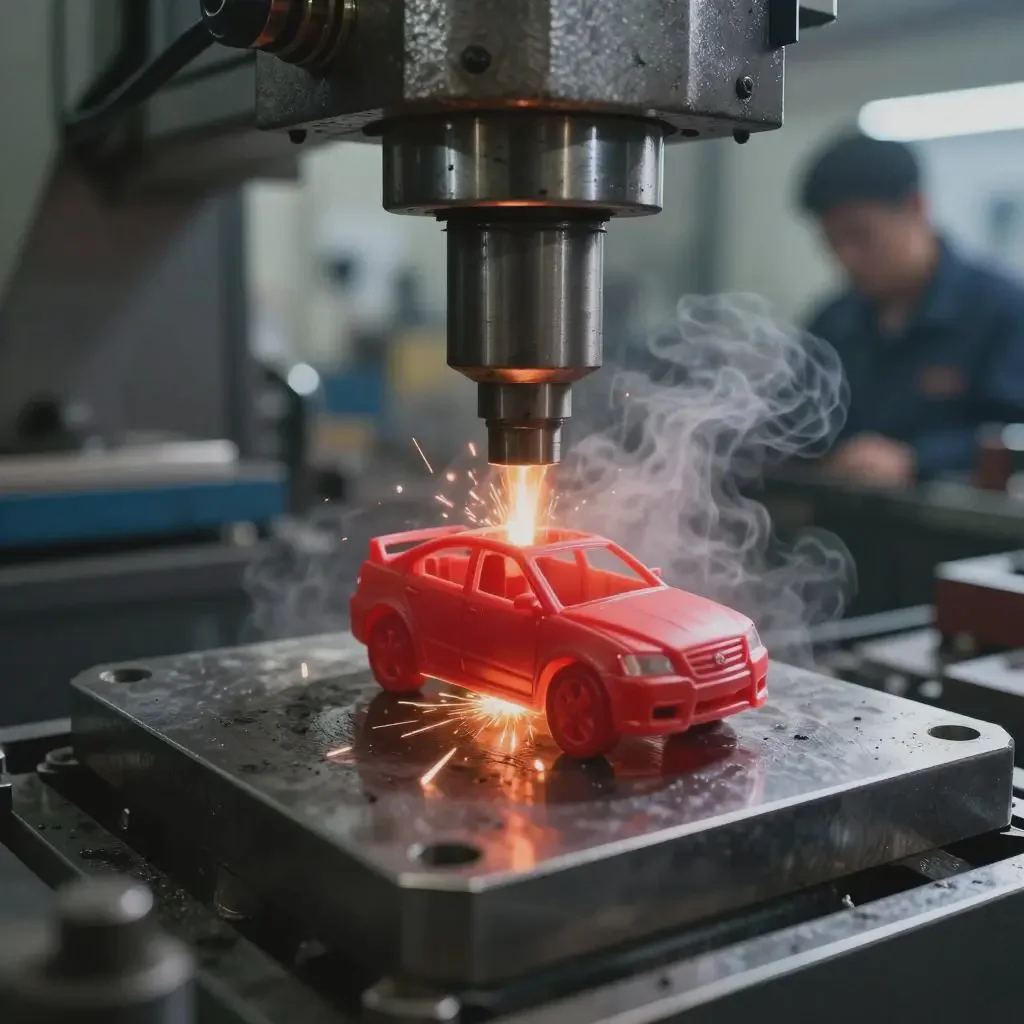
5. Mass Production
The scaled-up manufacturing process begins.
Injection Molding: Plastic granules are melted and injected into molds to create parts.
Decoration & Painting: Parts are decorated via pad printing, spray painting, or using molded colors.
Assembly: Components are assembled manually, via automated systems, or a combination. Electronics are installed, and sound modules are integrated.
Quality Control (QC) During Production: In-line QC checks occur at each stage (IQC, IPQC) to catch defects immediately.

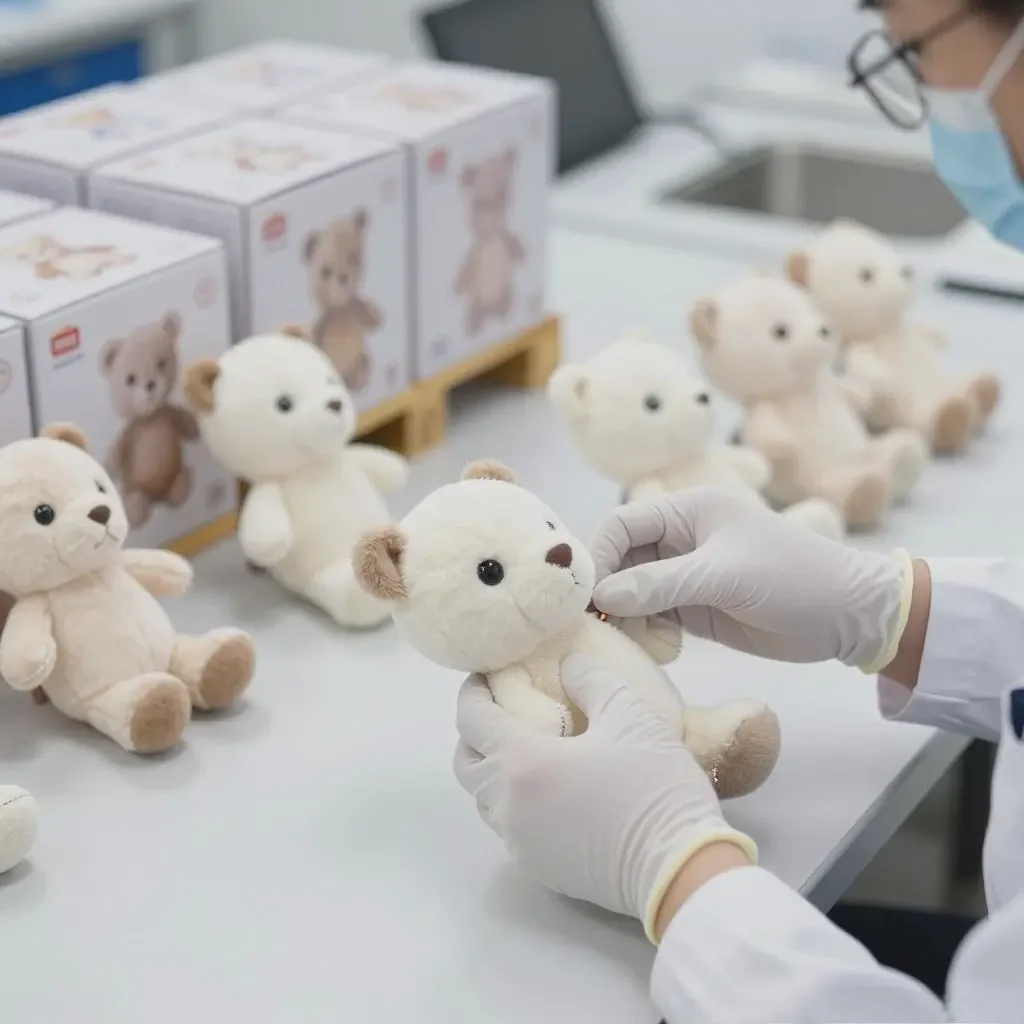
6. Final Assembly, Quality Assurance & Packaging
Preparing the finished product for shipment.
Final Assembly: Sub-assemblies come together for the final product.
Function Testing: A percentage of units from the line are randomly tested for full functionality.
Final Random Inspection (FRI): An AQL (Acceptable Quality Level) inspection is performed on packaged goods before shipping. This statistical sampling determines if the batch passes or fails.
Packaging: Toys are placed in blister packs, clamshells, or gift boxes, with all necessary labels, barcodes, and age warnings.

7. Logistics & Delivery
Getting the toys to your warehouse or distributor.
The OEM packs cartons onto pallets and loads shipping containers.
They handle export documentation and can assist with freight forwarding and customs clearance (Incoterms dependent).
Best Practices for a Successful OEM Partnership
Clear Communication: Provide detailed, unambiguous specifications from day one.
Realistic Timelines: Account for 6-12 months from concept to shipment for a new, complex toy.
Invest in Quality: Never compromise on safety testing or material quality.
Visit the Factory: Conduct an on-site audit to assess capabilities, quality systems, and working conditions.
Plan for Iterations: Budget and schedule for multiple prototype revisions.
Conclusion
Navigating the OEM toy manufacturing process—from initial design to mass production—requires meticulous planning, a trusted manufacturing partner, and an unwavering commitment to safety and quality. By understanding and following this structured roadmap, brands can effectively manage risks, control costs, and successfully launch products that delight children and stand the test of the global market.
Dofollow:
European Commission - Toy Safety





